Chronic lower leg pain is common among athletes. Causes can include medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints) and stress fracture. Exercise-induced compartment syndrome is an uncommon diagnosis that also needs to be considered, particularly in running sports.
This condition, which can be chronic, occurs when adequate blood flow does not reach specific closed compartments within the lower leg. The compartments contain muscles and boundaries composed of bone and rigid fascia (layers of connective tissue). During physical activity, muscle volume can increase up to 20 percent. Muscles that enlarge inside these unyielding compartments increase pressure and inhibit muscular blood flow. The result is aching and burning pain and possibly numbness and weakness.
One sign of exercise-induced compartment syndrome is that leg pain is completely relieved when the activity is stopped. If numbness and weakness are present, these also resolve quickly. Another sign is that the athlete can often pinpoint the moment that pain begins during exercise. In contrast, pain from shin splints or stress fracture will typically persist to some extent during rest.
During a physical exam for exercise-induced compartment syndrome, the affected area usually feels normal, without tenderness to palpation. In contrast, a physical exam for shin splints or stress fracture will often demonstrate tenderness over the bone or fascia.
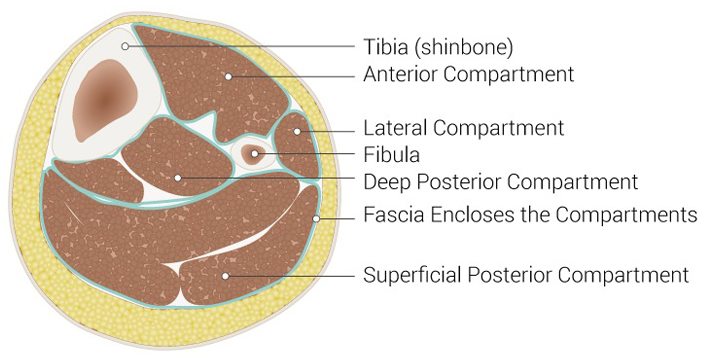
Leg Compartments
Of the four compartments in the lower leg (anterior, lateral, superficial, and deep posterior), the anterior compartment is most frequently involved. A diagnosis is confirmed by measuring compartment pressures at rest and after exercise.
Treatment usually requires the athlete to modify or give up the sport or undergo surgical treatment. Unfortunately, nonsurgical treatment is generally ineffective. Surgery involves the fascial release of the involved compartment and is 90 percent effective in getting athletes back to their sport.
About David Grauer, MD
Orthopedics & Sports Medicine at Boulder Medical Center
 As a board-certified orthopedic specialist and sports medicine physician, Dr. Grauer enjoys helping his patients, who are often athletes of all levels, return to their sports and activities as quickly and safely as possible.
As a board-certified orthopedic specialist and sports medicine physician, Dr. Grauer enjoys helping his patients, who are often athletes of all levels, return to their sports and activities as quickly and safely as possible.

